Unveiling the Political Landscape of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Continent’s Divisions
Related Articles: Unveiling the Political Landscape of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Continent’s Divisions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Political Landscape of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Continent’s Divisions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Political Landscape of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Continent’s Divisions

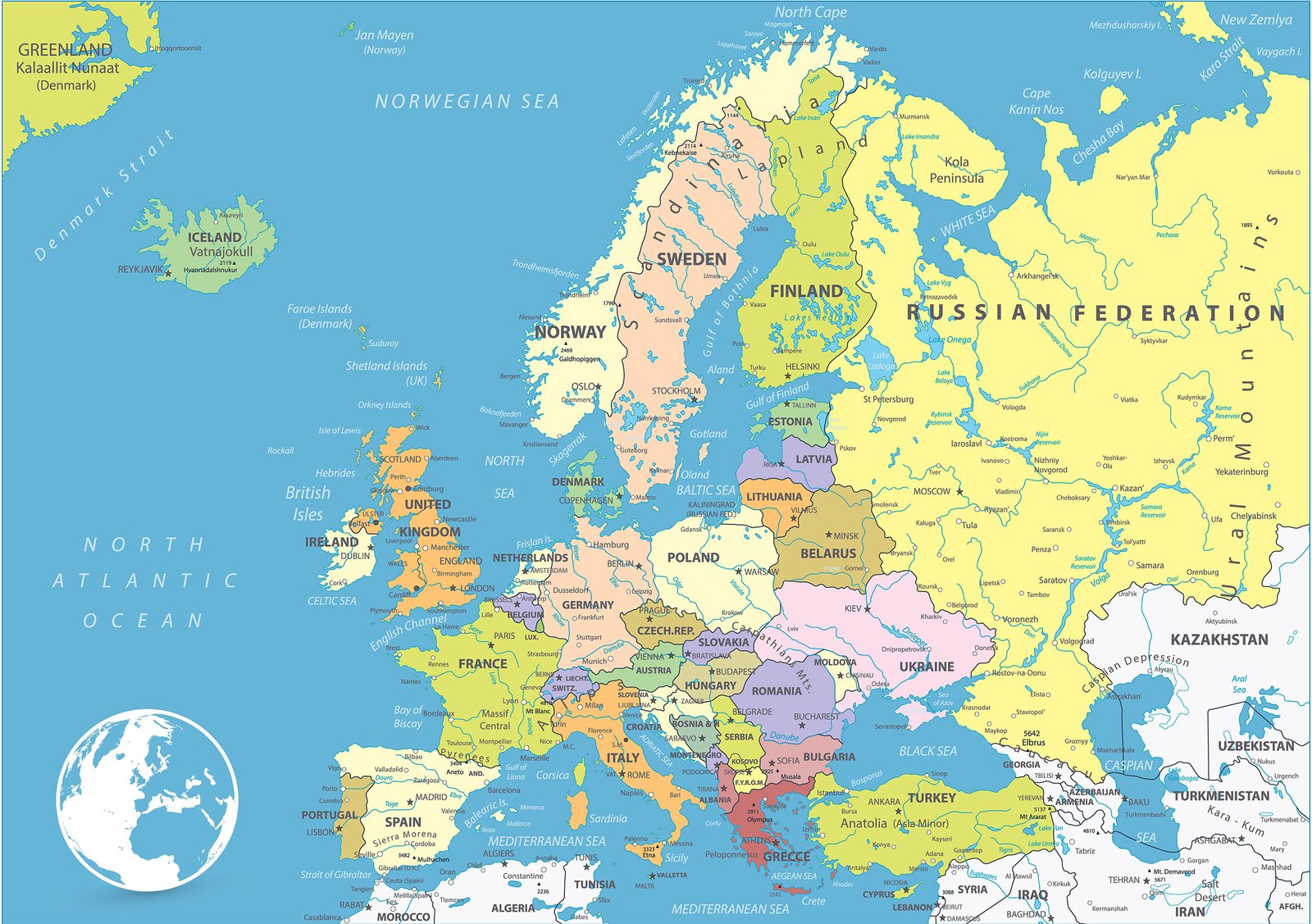
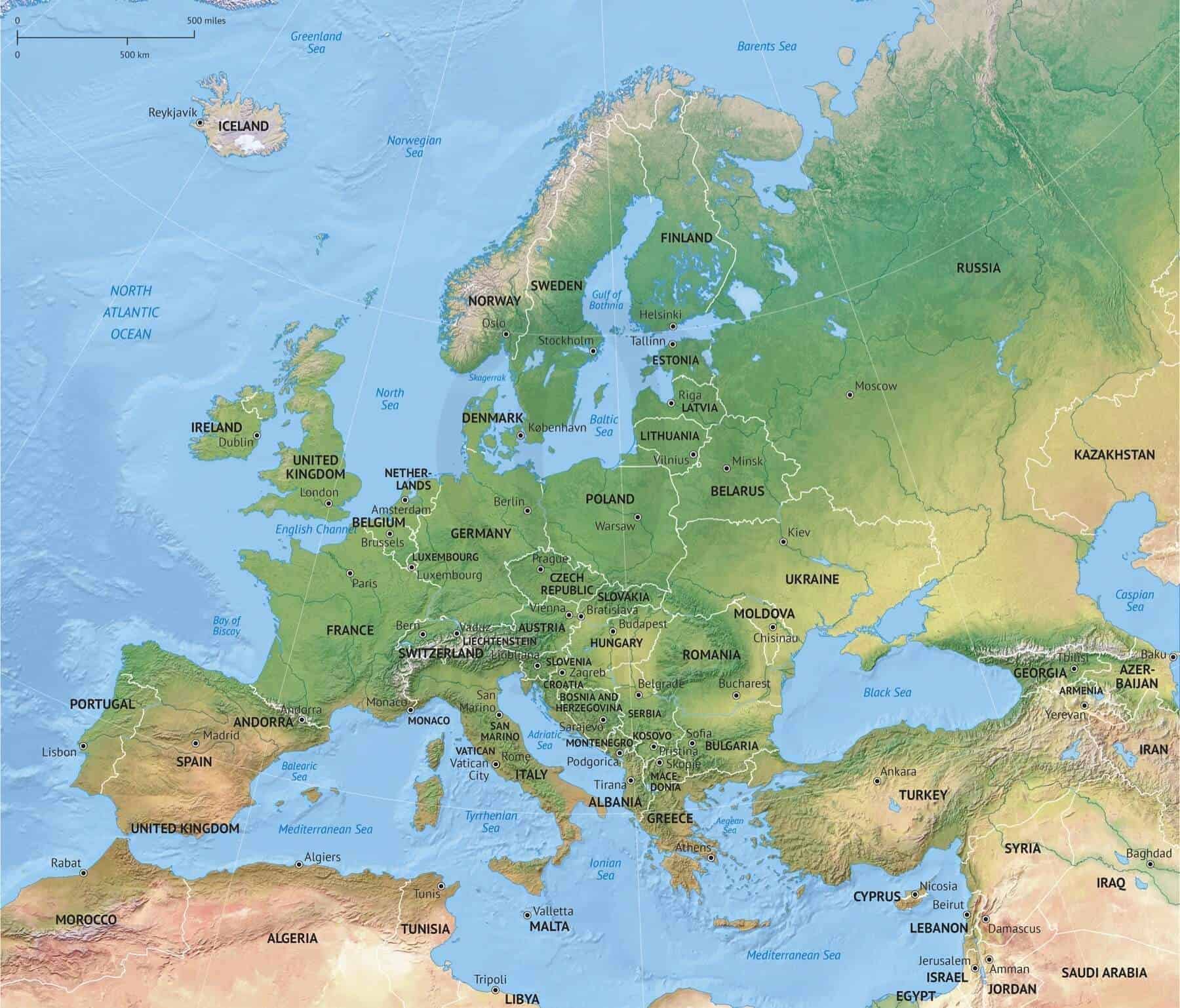
Europe, a continent rich in history, culture, and diverse landscapes, is also characterized by a complex and ever-evolving political landscape. Understanding the political map of Europe is crucial for comprehending the continent’s dynamics, its historical trajectory, and its future potential. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed analysis of the political map of Europe, exploring its intricacies, its evolution, and its implications for global affairs.
The Evolution of European Borders:
The political map of Europe has undergone significant transformations throughout history. From the ancient Roman Empire to the fall of the Soviet Union, the continent has witnessed numerous shifts in power, territorial adjustments, and the rise and fall of empires. The current map, a product of centuries of political and social evolution, reflects a tapestry of historical events, cultural identities, and political ideologies.
Key Features of the Political Map:
- National Borders: Europe is divided into 44 sovereign states, each with its own defined territory, government, and legal system. These national borders are often the result of historical agreements, wars, and political negotiations, reflecting the complex tapestry of European history.
- EU Membership: The European Union (EU), a political and economic union of 27 member states, plays a significant role in shaping the political map of Europe. The EU’s expansion has led to increased integration and cooperation among its member states, fostering economic growth and promoting political stability.
- Regional Differences: Despite its apparent homogeneity, Europe exhibits significant regional differences in terms of political systems, economic development, and cultural identity. These variations are reflected in the political map, highlighting the diverse nature of the continent.
- Internal Divisions: Within individual countries, political divisions can exist along ethnic, linguistic, or religious lines. These internal divisions can sometimes lead to political instability and even conflict, highlighting the complexities of managing diverse populations within a single state.
Understanding the Political Map’s Significance:
The political map of Europe is not merely a static representation of borders; it serves as a vital tool for understanding:
- Political Power Dynamics: The distribution of power across Europe is reflected in the size and influence of individual states. Understanding the political map allows for analyzing alliances, rivalries, and the shifting balance of power within the continent.
- Economic Integration: The EU’s influence on the political map has fostered economic integration, creating a single market and promoting trade and investment within its member states. This integration has contributed to economic growth and stability, but also raises questions about sovereignty and national autonomy.
- Cultural Diversity: The political map reflects the rich tapestry of cultures that make up Europe. Understanding the historical and cultural factors that have shaped national borders helps us appreciate the continent’s diversity and the challenges of fostering unity amidst differences.
- International Relations: The political map of Europe is crucial for comprehending the continent’s role in global affairs. Its strategic location, its economic power, and its historical influence make it a key player in international relations, impacting global trade, security, and political stability.
Exploring the Political Map in Detail:
To gain a deeper understanding of the political map of Europe, it is essential to delve into the individual countries and their respective political systems, historical backgrounds, and current challenges.
A. Western Europe:
- France: A major power in Europe, France boasts a long history of political and cultural influence. Its political system is a semi-presidential republic, with a strong executive branch.
- Germany: A key economic powerhouse in Europe, Germany is a federal republic with a parliamentary system. Its history of reunification and its role in the EU have significantly shaped its political landscape.
- United Kingdom: Despite its recent exit from the EU, the UK remains a significant player in European politics. Its parliamentary system and its historical ties to the continent continue to influence its relationship with its neighbors.
- Spain: A diverse country with a rich history, Spain is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. Its recent economic challenges and the ongoing issue of Catalan independence have shaped its political landscape.
B. Central Europe:
- Poland: A large and influential country in Central Europe, Poland is a parliamentary republic. Its history of communist rule and its strong ties to the Catholic Church continue to influence its political scene.
- Czech Republic: A vibrant democracy, the Czech Republic has a parliamentary system. Its economic success and its role in the EU have transformed its political landscape since the Velvet Revolution.
- Hungary: A country with a complex history, Hungary is a parliamentary republic. Its recent political developments have raised concerns about democratic backsliding and the erosion of media freedom.
C. Eastern Europe:
- Russia: A vast and influential country spanning two continents, Russia is a semi-presidential republic. Its history of imperial expansion, its role in the Cold War, and its current geopolitical ambitions have shaped its relationship with Europe.
- Ukraine: A country caught in a geopolitical struggle, Ukraine is a semi-presidential republic. Its ongoing conflict with Russia has profound implications for its political stability and its future direction.
- Belarus: A country ruled by an authoritarian regime, Belarus is a presidential republic. Its close ties to Russia and its suppression of dissent have raised concerns about human rights and political freedom.
D. Southern Europe:
- Italy: A country with a rich cultural heritage, Italy is a parliamentary republic. Its political history is marked by instability and coalition governments, with challenges related to corruption and economic stagnation.
- Greece: A country with a long and turbulent history, Greece is a parliamentary republic. Its economic crisis in the 2010s has had a significant impact on its political landscape and its relationship with the EU.
- Portugal: A country with a strong sense of national identity, Portugal is a parliamentary republic. Its history of colonial expansion and its current economic challenges have shaped its political development.
E. Northern Europe:
- Sweden: A country known for its social welfare system and its commitment to neutrality, Sweden is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. Its role in the EU and its focus on environmental sustainability have shaped its political landscape.
- Norway: A wealthy country with a strong social welfare system, Norway is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. Its status as a non-EU member state and its focus on oil and gas production have influenced its political priorities.
- Finland: A country with a strong sense of national identity, Finland is a parliamentary republic. Its history of close ties to Russia and its economic success have shaped its political development.
FAQs about the Political Map of Europe:
Q: How has the political map of Europe changed over time?
A: The political map of Europe has undergone significant transformations throughout history, driven by factors such as war, political upheaval, and economic integration. The fall of the Roman Empire, the rise and fall of empires, and the Cold War have all had a profound impact on the continent’s borders.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the political map of Europe today?
A: The political map of Europe faces a range of challenges, including:
- Internal divisions: Ethnic, linguistic, and religious differences within countries can lead to political instability and conflict.
- Economic disparities: The gap between rich and poor countries within Europe can create tensions and undermine political stability.
- External threats: Russia’s aggressive foreign policy and the rise of populism and nationalism pose challenges to European security and unity.
- Migration: The ongoing migration crisis has placed strain on political systems and challenged the concept of open borders within the EU.
Q: What is the future of the political map of Europe?
A: The future of the political map of Europe is uncertain, but several factors will likely play a significant role:
- The EU’s future: The EU’s ability to address the challenges it faces will determine its future influence on the political map of Europe.
- Russia’s role: Russia’s geopolitical ambitions and its relationship with Europe will continue to shape the continent’s political landscape.
- Populism and nationalism: The rise of these forces could lead to further fragmentation and instability within Europe.
- Technological advancements: Technological changes, such as artificial intelligence and automation, will have an impact on the political map of Europe, potentially creating new challenges and opportunities.
Tips for Understanding the Political Map of Europe:
- Study historical maps: Examining historical maps can help you understand the evolution of European borders and the factors that have shaped the current political landscape.
- Research individual countries: Delve into the political systems, historical backgrounds, and current challenges of individual countries to gain a deeper understanding of their role in the European context.
- Follow news and events: Stay informed about current events and political developments in Europe to stay up-to-date on the changing political landscape.
- Engage in discussions: Participate in discussions about European politics and share your perspectives with others.
Conclusion:
The political map of Europe is a dynamic and complex entity, reflecting a rich tapestry of history, culture, and political ideologies. Understanding its evolution, its key features, and its significance for global affairs is essential for comprehending the continent’s present and its potential future. By exploring the individual countries and their political systems, by analyzing the challenges and opportunities facing Europe, and by engaging in informed discussions about its political landscape, we can gain a deeper appreciation for this fascinating and ever-changing continent.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Political Landscape of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Continent’s Divisions. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!