Understanding the Honda 3-Bar MAP Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Honda 3-Bar MAP Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Honda 3-Bar MAP Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Honda 3-Bar MAP Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide
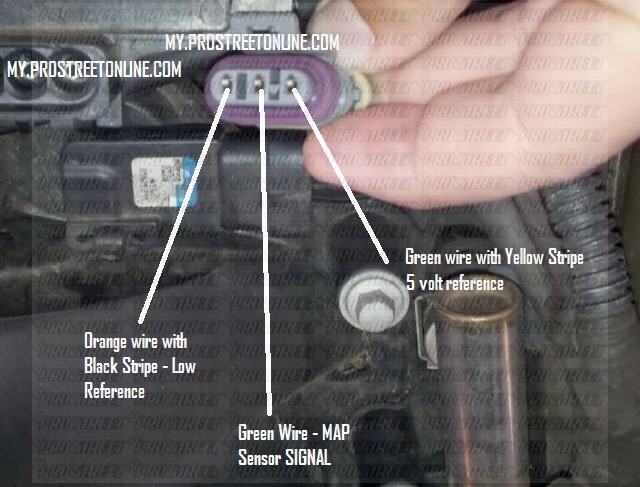
The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is a crucial component in modern automotive engine management systems. It plays a vital role in determining the amount of air entering the engine, influencing fuel injection, ignition timing, and ultimately, engine performance. In Honda vehicles, a specific type of MAP sensor, known as the 3-bar MAP sensor, is commonly found in performance-oriented models, particularly those equipped with turbochargers. This article delves into the workings of the Honda 3-bar MAP sensor, its significance, potential issues, and maintenance tips.
The Role of the MAP Sensor in Engine Management
The MAP sensor’s primary function is to measure the pressure inside the intake manifold. This pressure, known as manifold absolute pressure, is directly related to the amount of air being drawn into the engine. The sensor converts this pressure into an electrical signal, which is then transmitted to the engine control unit (ECU).
The ECU utilizes this information to:
- Calculate the air mass: The ECU uses the MAP sensor reading alongside other parameters like engine speed and temperature to calculate the precise amount of air entering the engine.
- Adjust fuel injection: Based on the air mass calculation, the ECU determines the appropriate amount of fuel to inject for optimal combustion.
- Optimize ignition timing: The MAP sensor data also helps the ECU adjust ignition timing for maximum efficiency and power.
- Control other engine parameters: The MAP sensor reading can also influence other engine parameters like idle speed, throttle response, and emissions control.
Why the 3-Bar MAP Sensor?
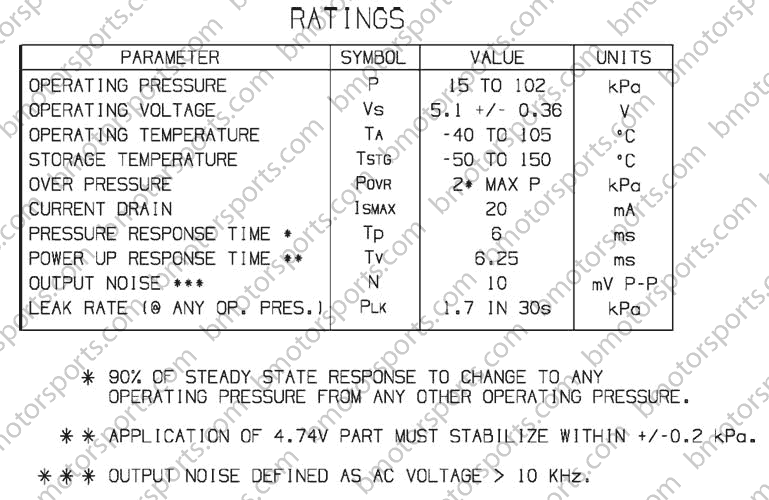
The "bar" in the 3-bar MAP sensor refers to the pressure range it can measure. A 3-bar MAP sensor is capable of measuring pressures up to approximately 43.5 psi (3 bar), while a standard 1-bar MAP sensor typically measures up to 14.5 psi (1 bar).
The higher pressure range of the 3-bar MAP sensor is particularly beneficial in turbocharged engines. Turbochargers force air into the intake manifold, significantly increasing the pressure within the system. A standard 1-bar MAP sensor would struggle to accurately measure these higher pressures, leading to inaccurate engine control and potentially detrimental effects on performance.
The Benefits of the 3-Bar MAP Sensor in Turbocharged Honda Vehicles:
- Precise air mass calculation: The wider pressure range allows for more accurate measurement of the air entering the engine, even under boosted conditions.
- Optimized fuel delivery: Precise air mass calculation leads to more accurate fuel delivery, maximizing combustion efficiency and power output.
- Enhanced throttle response: The ECU can respond more effectively to changes in throttle position, resulting in a quicker and more responsive acceleration.
- Improved engine performance: The combination of accurate air mass measurement, optimized fuel delivery, and enhanced throttle response contributes to a noticeable improvement in overall engine performance.
Common Issues with the Honda 3-Bar MAP Sensor
While the 3-bar MAP sensor is a robust component, it can still experience issues over time. Here are some common problems:
- Vacuum leaks: A vacuum leak in the intake manifold can affect the pressure readings, leading to inaccurate sensor data.
- Contamination: Dirt, debris, or oil buildup on the sensor can interfere with its operation.
- Electrical faults: Faulty wiring, connectors, or internal sensor components can disrupt the signal transmission.
- Sensor failure: The sensor itself may fail due to age, wear, or environmental factors.
Symptoms of a Faulty 3-Bar MAP Sensor
A faulty 3-bar MAP sensor can manifest itself in various symptoms:
- Rough idling: The engine may idle erratically or stall due to incorrect fuel delivery.
- Hesitation during acceleration: The engine may hesitate or stumble when accelerating, especially under boost.
- Reduced power output: The engine may experience a noticeable loss of power.
- Increased fuel consumption: Incorrect air mass calculation can lead to excessive fuel consumption.
- Check engine light: The ECU may detect a malfunctioning sensor and illuminate the check engine light.
Diagnosing and Replacing the 3-Bar MAP Sensor
If you suspect a problem with the 3-bar MAP sensor, it’s essential to diagnose the issue accurately. Here’s a general approach:
- Visual inspection: Check the sensor for signs of damage, contamination, or loose connections.
- Vacuum leak test: Inspect the intake manifold for any leaks that could affect the pressure readings.
- Diagnostic scan: Use an OBD-II scanner to read any error codes related to the MAP sensor.
- Pressure test: Use a pressure gauge to verify the sensor’s readings against known pressure values.
If the diagnosis confirms a faulty 3-bar MAP sensor, replacing it is crucial to restore proper engine operation. Here’s a general guideline for replacement:
- Locate the sensor: The 3-bar MAP sensor is usually located on the intake manifold, near the throttle body or air intake.
- Disconnect the electrical connector: Unplug the sensor’s electrical connector.
- Remove the sensor: Carefully remove the sensor from its mounting location.
- Install the new sensor: Install the new sensor securely in the same location.
- Reconnect the electrical connector: Plug the electrical connector back into the sensor.
- Clear error codes: After installation, use an OBD-II scanner to clear any stored error codes.
FAQs Regarding the Honda 3-Bar MAP Sensor
Q: How often should I replace the 3-bar MAP sensor?
A: There’s no fixed replacement schedule for the 3-bar MAP sensor. Its lifespan depends on various factors, including driving conditions, maintenance, and environmental exposure. However, it’s generally recommended to inspect the sensor periodically for signs of wear or damage.
Q: Can I use a 1-bar MAP sensor instead of a 3-bar MAP sensor in a turbocharged Honda?
A: No, using a 1-bar MAP sensor in a turbocharged Honda with a 3-bar MAP sensor requirement will result in inaccurate engine control and potentially damage the engine. The ECU is programmed to work with a specific type of MAP sensor, and using an incompatible sensor can lead to serious problems.
Q: Can I clean the 3-bar MAP sensor?
A: Cleaning the 3-bar MAP sensor is not recommended. Attempting to clean the sensor can damage its sensitive components and may not effectively remove contaminants. If you suspect contamination, it’s best to replace the sensor entirely.
Q: What are the signs of a vacuum leak affecting the 3-bar MAP sensor?
A: A vacuum leak can cause erratic engine behavior, including rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, and reduced power. It can also affect fuel economy and emissions.
Q: How do I test the 3-bar MAP sensor?
A: Testing the 3-bar MAP sensor involves verifying its readings against known pressure values. This can be done using a pressure gauge and a vacuum pump to simulate different pressure conditions.
Tips for Maintaining the Honda 3-Bar MAP Sensor
- Regular maintenance: Perform routine inspections of the 3-bar MAP sensor for signs of damage, contamination, or loose connections.
- Avoid excessive engine revving: Frequent high-rpm driving can put extra stress on the sensor and shorten its lifespan.
- Use high-quality engine oil: Dirty or contaminated oil can find its way to the sensor, affecting its performance.
- Replace air filter regularly: A dirty air filter can restrict airflow and affect the sensor’s readings.
- Keep the engine bay clean: Avoid excessive dirt and debris buildup in the engine bay, which can contaminate the sensor.
Conclusion
The Honda 3-bar MAP sensor plays a critical role in optimizing engine performance, particularly in turbocharged models. Understanding its function, potential issues, and maintenance tips can help ensure proper engine operation and prevent costly repairs. By addressing any problems promptly and maintaining the sensor properly, you can maximize your Honda’s performance and longevity.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Honda 3-Bar MAP Sensor: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!