Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to 5 Essential Map Types
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to 5 Essential Map Types
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to 5 Essential Map Types. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to 5 Essential Map Types
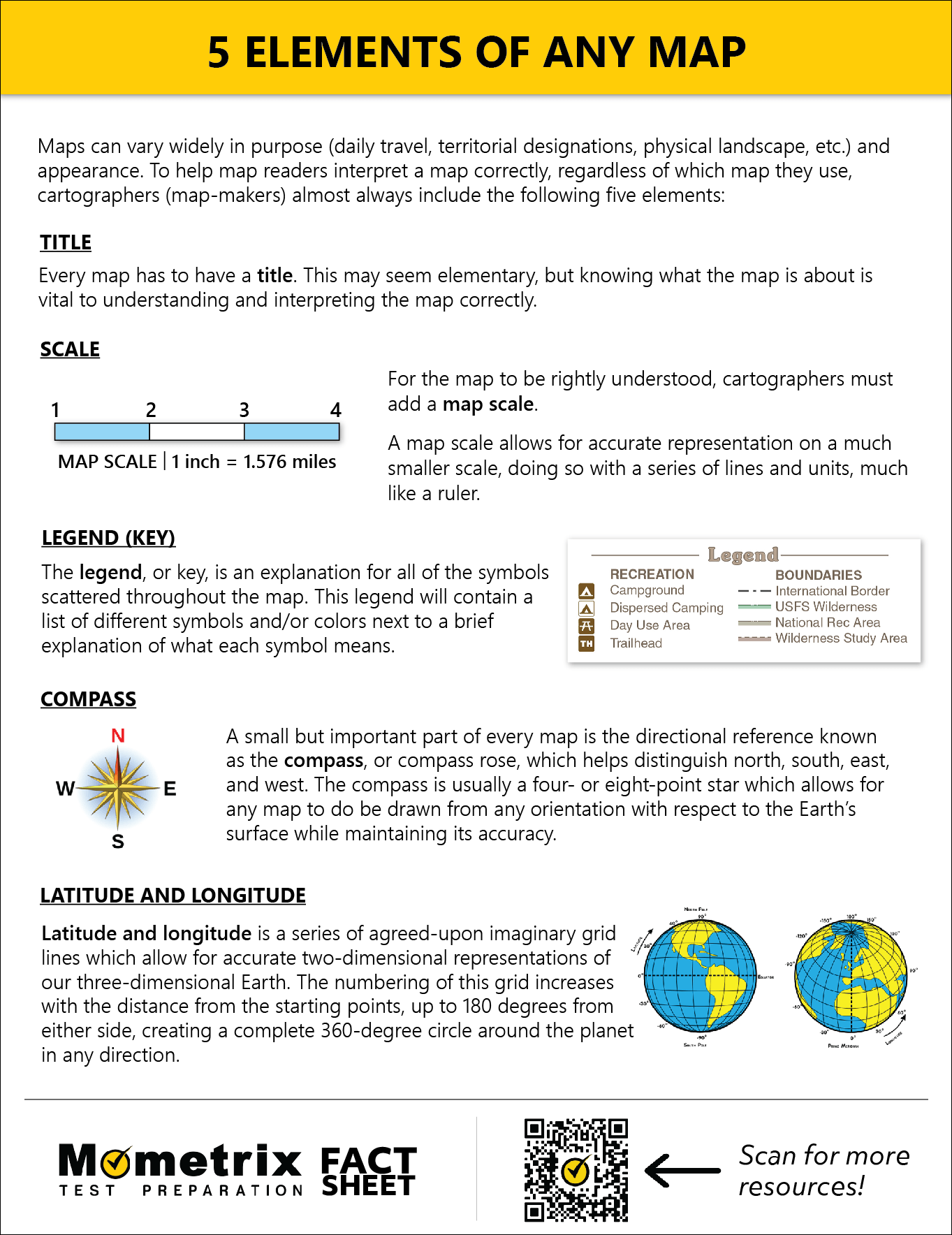
Maps are more than just static representations of the world; they are powerful tools for understanding and navigating our planet. They provide a visual framework for comprehending spatial relationships, aiding in exploration, planning, and decision-making across various disciplines. This comprehensive guide delves into five essential map types, exploring their unique characteristics, benefits, and applications.
1. Topographic Maps: Unveiling the Earth’s Topography
Topographic maps, also known as contour maps, are indispensable for depicting the Earth’s surface with remarkable detail. They use contour lines to represent elevation changes, creating a three-dimensional visual representation of the terrain. Each contour line connects points of equal elevation, providing a precise understanding of the landscape’s form.
Understanding the Benefits:
- Detailed Terrain Representation: Topographic maps offer a comprehensive view of the terrain, including hills, valleys, mountains, and other landforms. This detailed information is crucial for various activities, such as hiking, camping, and construction.
- Elevation Measurement: Contour lines allow for accurate elevation measurement, enabling users to determine the height of specific points on the map. This information is essential for tasks such as route planning, resource management, and infrastructure development.
- Slope and Aspect Analysis: The spacing and direction of contour lines reveal the steepness and orientation of slopes. This information is vital for understanding drainage patterns, geological formations, and potential hazards.
FAQs:
- What are contour lines? Contour lines are lines on a topographic map that connect points of equal elevation.
- How are topographic maps used in real-world applications? Topographic maps are widely used in fields like surveying, geology, forestry, and urban planning. They are essential for tasks such as land development, resource management, and disaster preparedness.
- What are the limitations of topographic maps? Topographic maps are static representations of the Earth’s surface and do not account for dynamic changes, such as weather patterns or vegetation growth.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps:
- Understand the contour interval: The contour interval indicates the difference in elevation between adjacent contour lines.
- Recognize the features of the terrain: Steep slopes are represented by closely spaced contour lines, while gentle slopes have widely spaced lines.
- Use the map in conjunction with other sources of information: Combining topographic maps with satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and local knowledge enhances situational awareness.
2. Thematic Maps: Unveiling Patterns and Relationships
Thematic maps are designed to showcase a specific theme or attribute, highlighting patterns and relationships within a given area. Unlike topographic maps that focus on terrain, thematic maps use symbols, colors, and patterns to represent data related to population density, rainfall distribution, or economic activity.
Understanding the Benefits:
- Data Visualization: Thematic maps effectively visualize complex data, making it easier to understand trends, patterns, and anomalies. This visual representation facilitates analysis and decision-making.
- Spatial Relationships: Thematic maps highlight spatial relationships between different variables, revealing connections and interactions that might otherwise be overlooked.
- Targeted Communication: Thematic maps are valuable tools for communicating complex information to a broad audience, especially those without specialized knowledge.
FAQs:
- What are the different types of thematic maps? Common types include choropleth maps (using color shades to represent data), dot density maps (using dots to represent data points), and proportional symbol maps (using symbols of varying sizes to represent data).
- How are thematic maps used in real-world applications? Thematic maps are widely used in fields like public health, environmental studies, and urban planning. They are valuable for understanding population demographics, disease outbreaks, and resource allocation.
- What are the challenges of creating thematic maps? Thematic maps can be influenced by data quality, map projections, and the chosen symbology. Careful consideration of these factors is crucial for accurate and effective representation.
Tips for Interpreting Thematic Maps:
- Pay attention to the legend: The legend explains the symbology used on the map, ensuring accurate data interpretation.
- Consider the scale and projection: The map’s scale and projection can influence the visual representation of data.
- Analyze the patterns and trends: Look for clusters, outliers, and spatial correlations to understand the data’s underlying patterns.
3. Road Maps: Navigating the Network of Roads
Road maps are essential tools for navigating the world’s intricate network of roads and highways. These maps typically feature detailed information about road types, distances, and points of interest, providing a clear visual guide for travelers.
Understanding the Benefits:
- Route Planning: Road maps assist in planning journeys by providing a comprehensive overview of the available routes and their estimated distances.
- Point-to-Point Navigation: Road maps enable users to easily navigate between specific locations, identifying the most efficient and convenient paths.
- Local Information: Road maps often include information about points of interest, such as gas stations, restaurants, and accommodations, enhancing the travel experience.
FAQs:
- What are the different types of road maps? Road maps can be printed, digital, or interactive, offering various levels of detail and functionality.
- How have road maps evolved with technology? Modern road maps utilize GPS technology and digital mapping software, providing real-time navigation and traffic updates.
- What are the limitations of traditional road maps? Traditional road maps are static and do not account for dynamic factors such as traffic conditions or road closures.
Tips for Using Road Maps:
- Choose the appropriate scale: Select a map with a scale that provides sufficient detail for the intended journey.
- Familiarize yourself with the legend: Understand the symbols and abbreviations used to represent different road types and points of interest.
- Plan your route in advance: Identify alternative routes and consider potential traffic congestion or road closures.
4. Navigation Maps: Guiding You to Your Destination
Navigation maps, often integrated with GPS technology, provide real-time guidance and directions to users. These maps dynamically adjust to traffic conditions, road closures, and other real-time factors, ensuring the most efficient and up-to-date route.
Understanding the Benefits:
- Real-Time Guidance: Navigation maps provide turn-by-turn directions, constantly adjusting to changing road conditions and providing the most efficient route.
- Traffic Awareness: These maps integrate with traffic data, alerting users to congestion and suggesting alternative routes to avoid delays.
- Point-of-Interest Discovery: Navigation maps often include information about nearby points of interest, such as restaurants, hotels, and attractions.
FAQs:
- What are the different types of navigation maps? Navigation maps are available as standalone devices, smartphone apps, and integrated systems in vehicles.
- How do navigation maps utilize GPS technology? GPS technology allows navigation maps to determine the user’s location and provide accurate directions.
- What are the challenges of using navigation maps? Navigation maps rely on accurate data and can be affected by signal loss, outdated information, and unexpected road closures.
Tips for Using Navigation Maps:
- Ensure a strong GPS signal: A strong signal ensures accurate location determination and route guidance.
- Update the map data regularly: Keep the map data up-to-date to account for road changes and traffic conditions.
- Consider alternative routes: Explore alternative routes suggested by the navigation map to avoid traffic congestion.
5. Climate Maps: Unveiling the World’s Climate Patterns
Climate maps depict the Earth’s climate patterns, providing a visual representation of temperature, precipitation, and other climatic variables. These maps are crucial for understanding the global climate system and its impact on various aspects of human life.
Understanding the Benefits:
- Climate Pattern Visualization: Climate maps visually represent the distribution of climatic variables, revealing patterns and trends across different regions.
- Climate Change Analysis: Climate maps are valuable tools for analyzing climate change impacts, tracking shifts in temperature, precipitation, and other climatic factors.
- Resource Management: Climate maps inform resource management strategies, helping to understand water availability, agricultural potential, and the impact of climate variability on ecosystems.
FAQs:
- What are the different types of climate maps? Climate maps can depict various variables, including temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and humidity.
- How are climate maps used in real-world applications? Climate maps are used by researchers, policymakers, and businesses to understand climate trends, assess climate change impacts, and develop mitigation strategies.
- What are the challenges of creating accurate climate maps? Climate data collection, analysis, and projection are complex processes, and climate maps can be influenced by data limitations, model uncertainties, and the chosen time scale.
Tips for Interpreting Climate Maps:
- Understand the legend: The legend explains the symbology used to represent different climate variables.
- Consider the time scale: Climate maps can depict data over various time scales, from daily to long-term averages.
- Analyze the spatial patterns: Look for trends, anomalies, and regional variations in climate variables.
Conclusion:
From depicting the Earth’s topography to visualizing climate patterns, maps play a vital role in understanding and navigating our world. Each map type serves a unique purpose, providing valuable insights and tools for exploration, planning, and decision-making. By understanding the characteristics, benefits, and applications of different map types, individuals and organizations can leverage their power to make informed choices and navigate the complexities of our ever-changing world.




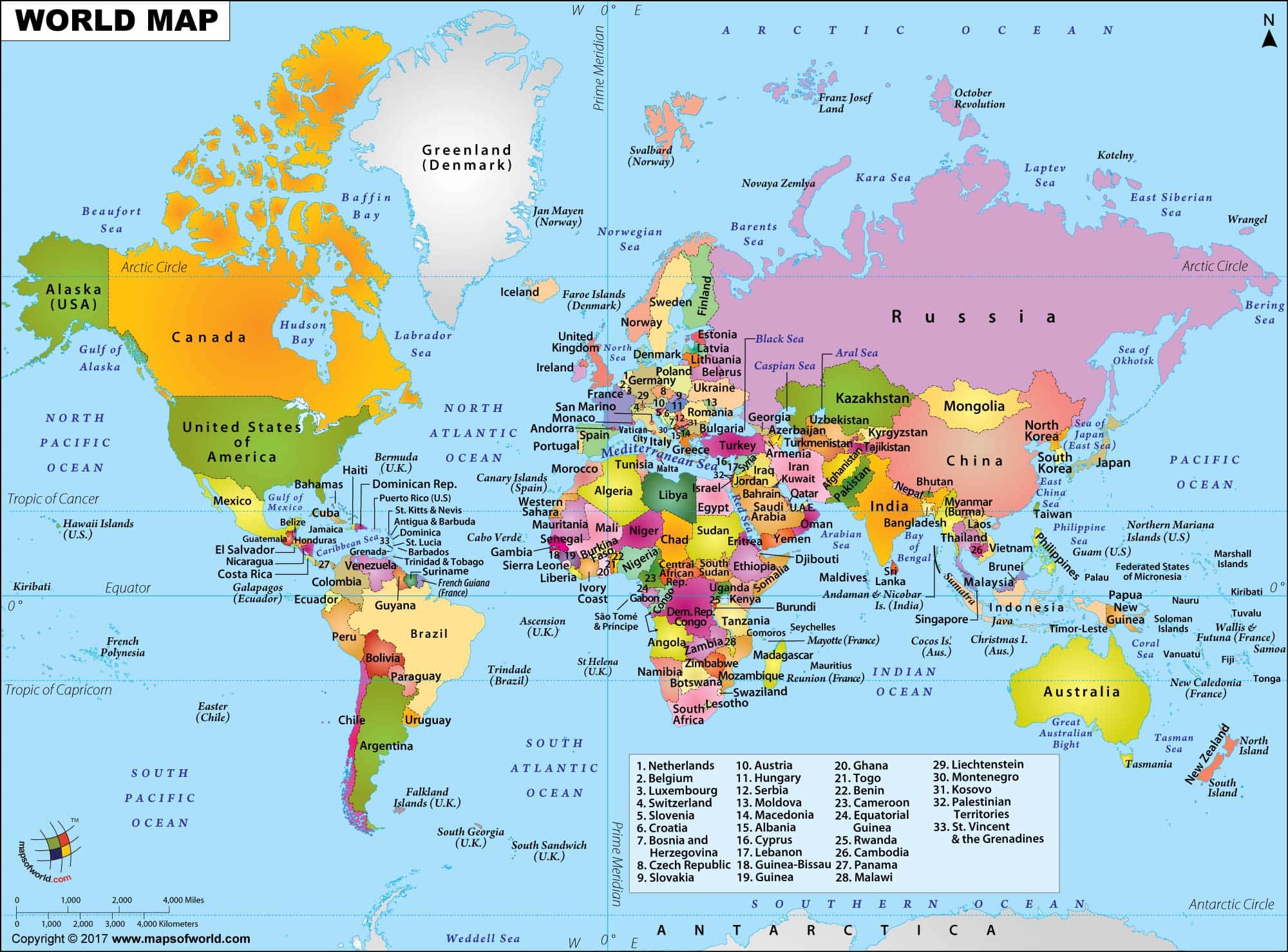


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to 5 Essential Map Types. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!