Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Virginia’s Plant Hardiness Zones
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Virginia’s Plant Hardiness Zones
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Virginia’s Plant Hardiness Zones. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Virginia’s Plant Hardiness Zones
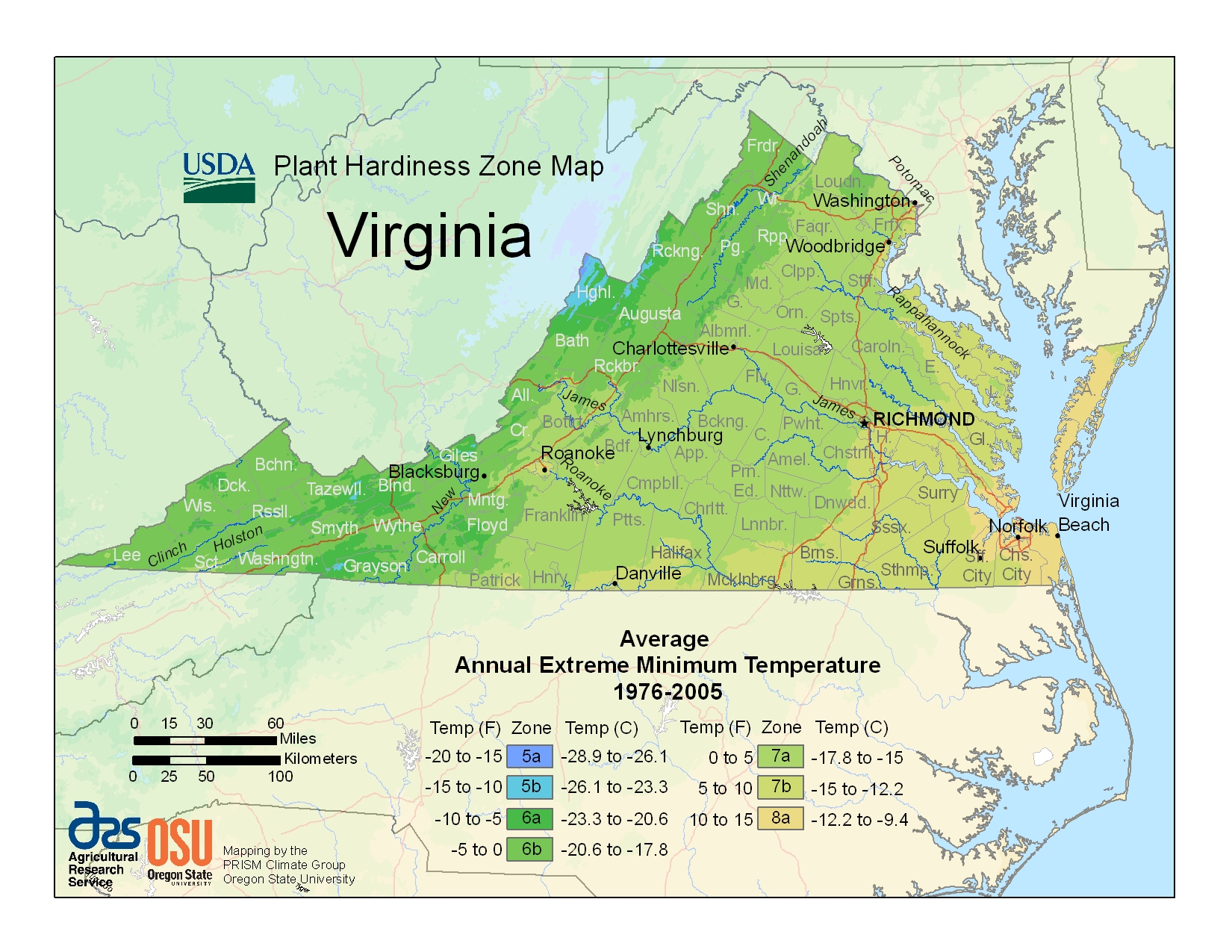
The Virginia Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable tool for gardeners, landscapers, and anyone interested in cultivating plants in the Commonwealth. This map, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), provides a visual representation of the average minimum winter temperatures across the state. This information is crucial for selecting plant varieties that can thrive in specific geographic locations, ensuring successful growth and minimizing the risk of winter damage.
Delving into the Zone System
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides the United States into 11 zones, each representing a 10-degree Fahrenheit difference in average minimum winter temperatures. Virginia, with its diverse topography and microclimates, spans multiple zones, ranging from Zone 6a in the western mountains to Zone 8a along the coastal plain.
Understanding Virginia’s Zone Variations
The variations in Virginia’s plant hardiness zones are attributed to several factors:
- Elevation: Higher elevations experience colder temperatures, leading to lower zone numbers. The Blue Ridge Mountains, for instance, fall within Zone 6a, while the coastal plains enjoy warmer temperatures, falling into Zone 8a.
- Proximity to Water: Large bodies of water, such as the Chesapeake Bay, moderate temperatures, creating a warmer microclimate and pushing zones towards higher numbers.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: Urban areas tend to be warmer than surrounding rural areas due to heat generated by buildings and infrastructure. This effect can shift zones slightly, making certain urban areas fall within a higher zone than their surrounding rural counterparts.
Utilizing the Virginia Zone Map for Successful Gardening
The Virginia Plant Hardiness Zone Map serves as a fundamental tool for informed gardening decisions. By understanding the zone associated with a particular location, gardeners can select plants that are well-suited to the local climate. This approach ensures that plants have a higher probability of survival and flourishing, maximizing the potential for a thriving garden.
- Choosing the Right Plants: The zone map acts as a guide for selecting plants that can withstand the minimum winter temperatures in a given location. By selecting plants within the appropriate zone, gardeners can avoid the disappointment of winter damage and ensure their plants have the best chance of survival.
- Understanding Plant Hardiness: The zone map provides a framework for understanding the temperature tolerance of different plant species. This knowledge allows gardeners to make informed choices about which plants to cultivate and which to avoid, based on the specific climate of their location.
- Planning Garden Layout: The zone map can be used to plan garden layouts that take advantage of microclimates within a property. For example, a gardener in a zone 7 area could create a section for zone 6 plants in a slightly cooler, shaded location, expanding the variety of plants that can be grown.
Beyond the Basics: Factors Beyond Zone
While the Virginia Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable starting point, other factors can influence plant success:
- Soil Type: The composition and quality of the soil play a significant role in plant growth. Factors like drainage, pH level, and nutrient content can affect plant health and survival.
- Sunlight Exposure: Different plants require varying amounts of sunlight. The amount of sunlight a location receives throughout the day is crucial for plant growth and development.
- Wind Exposure: Strong winds can cause damage to plants, especially during cold winters. Selecting wind-tolerant varieties or providing windbreaks can mitigate these effects.
- Local Microclimates: Variations in elevation, proximity to water, and urban heat island effects can create microclimates within a larger zone, influencing plant growth.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What if I live in a transition zone?
A: Transition zones occur between two main zones, indicating that the average minimum winter temperature falls between the two zone ranges. When choosing plants, gardeners in transition zones should consider the specific microclimate of their location and select plants that fall within the range of both zones.
Q: Can I grow plants outside of my zone?
A: While it is possible to grow plants outside of their recommended zone, it requires careful planning and additional care. This may involve providing protection from harsh winter conditions, selecting cold-hardy varieties, and ensuring proper soil conditions.
Q: How often is the Virginia Plant Hardiness Zone Map updated?
A: The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is updated periodically to reflect changes in climate patterns. However, the current map is a valuable tool for understanding the general climate conditions across Virginia.
Tips for Utilizing the Zone Map Effectively
- Consult Local Resources: In addition to the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, local nurseries and gardening organizations often provide specific recommendations for plants suited to the region.
- Observe Your Garden: Pay attention to the performance of different plants in your garden. This experience will help you refine your understanding of the local microclimate and adjust your plant selections accordingly.
- Embrace Experimentation: Gardening is an ongoing process of learning and experimentation. Don’t be afraid to try different plants and observe their growth and survival over time.
Conclusion: A Guide for Sustainable Gardening
The Virginia Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a powerful tool for gardeners and landscapers, offering a valuable framework for understanding the climate conditions of the Commonwealth. By utilizing the zone map and considering other factors like soil type, sunlight exposure, and wind exposure, gardeners can make informed plant selections, optimize their garden layouts, and maximize the potential for successful plant growth. Ultimately, this knowledge contributes to sustainable gardening practices, ensuring that plants thrive in their environment and contribute to the beauty and biodiversity of Virginia’s landscapes.




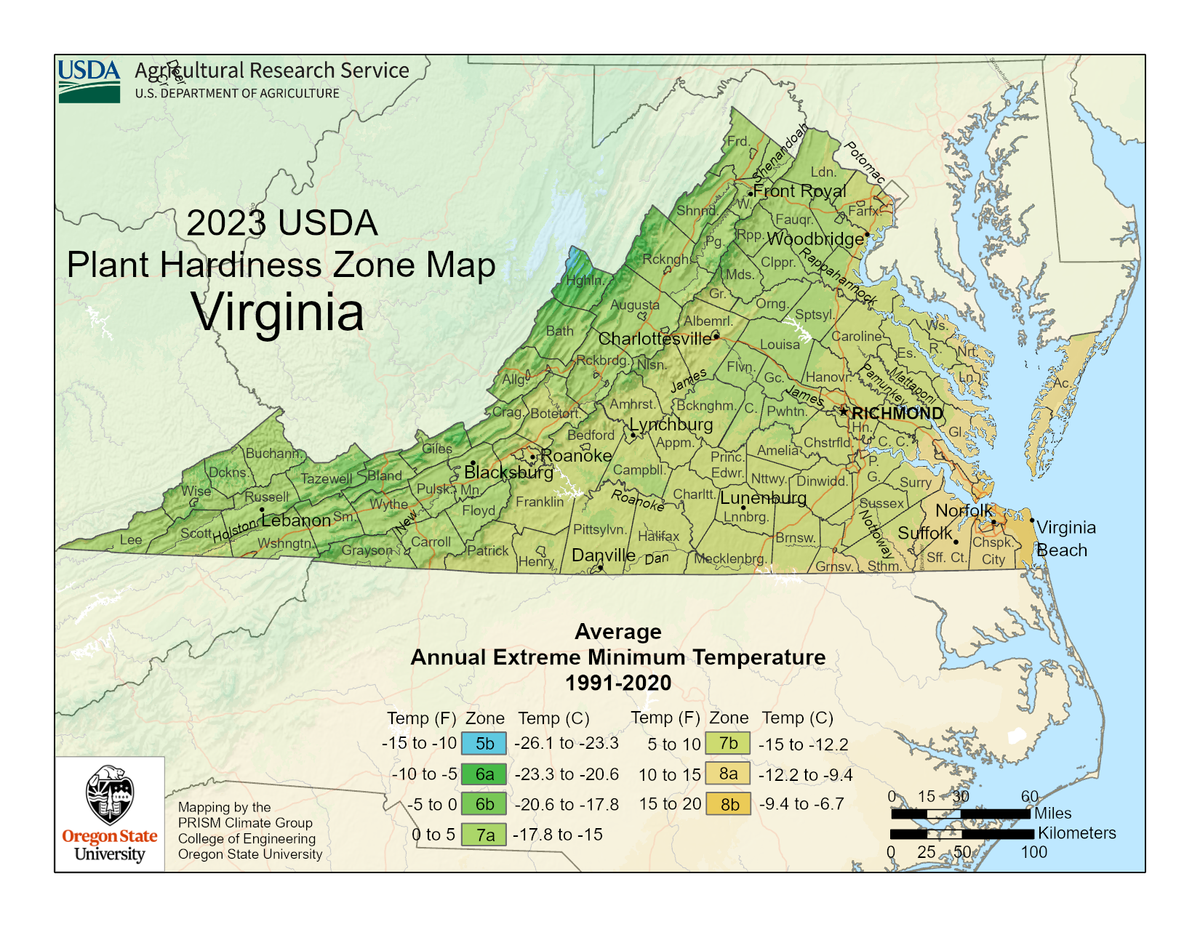

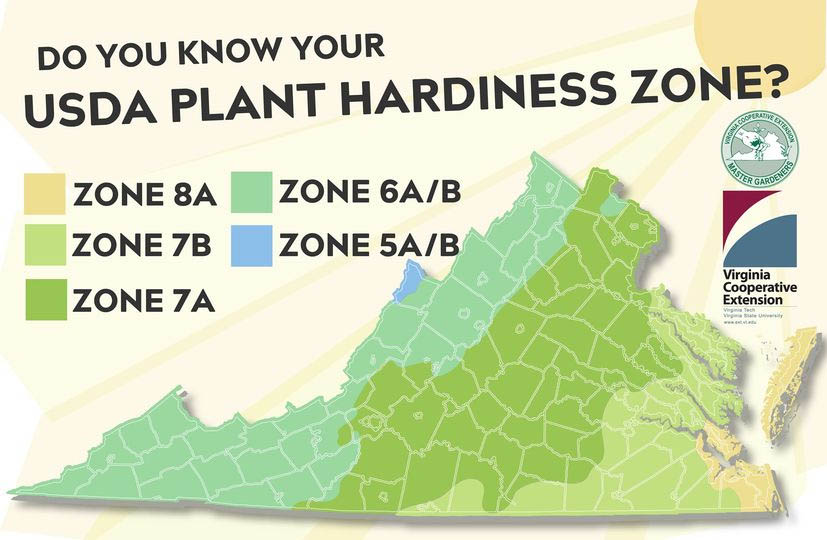

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Understanding Virginia’s Plant Hardiness Zones. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!