France’s Nuclear Power Landscape: A Map of Energy Independence and Environmental Impact
Related Articles: France’s Nuclear Power Landscape: A Map of Energy Independence and Environmental Impact
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to France’s Nuclear Power Landscape: A Map of Energy Independence and Environmental Impact. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
France’s Nuclear Power Landscape: A Map of Energy Independence and Environmental Impact
![Nuclear Power in France [OC] : r/MapPorn](https://i.redd.it/kmmksgyysmq41.png)
France stands out as a global leader in nuclear energy, with a vast network of nuclear power plants contributing significantly to its energy mix. This article delves into the intricate landscape of France’s nuclear power sector, exploring its geographical distribution, historical development, and the multifaceted implications of its reliance on this energy source.
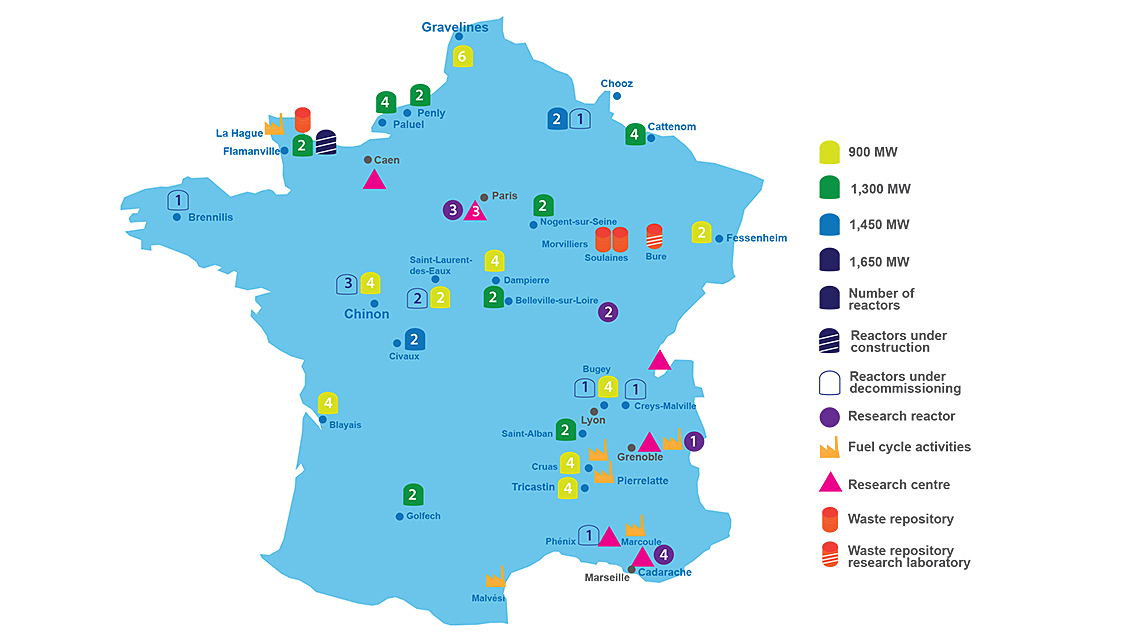
Mapping France’s Nuclear Power Plants
A glance at a map of France reveals a remarkable concentration of nuclear power plants along major rivers, particularly the Rhône, Loire, and Seine. This strategic placement reflects the crucial role of water in the cooling process of nuclear reactors.
Key Locations and their Significance:
-
Northern France: The northern region, home to major cities like Paris and Lille, houses several nuclear power plants, including:
- Fessenheim: This plant, located near the border with Germany, was the oldest in France and was permanently shut down in 2020.
- Nogent: Situated on the Seine River, this plant is a key contributor to the region’s energy supply.
- Gravelines: Located on the coast near the English Channel, this facility boasts six reactors and is one of the largest nuclear power plants in Europe.
-
Eastern France: The eastern region, bordering Germany and Switzerland, is another hub for nuclear energy production:
- Cattenom: This plant, on the Moselle River, is the largest in France and one of the most powerful in the world.
- Tricastin: Located in the Drôme department, this facility is known for its reprocessing plant and is a key player in the nuclear fuel cycle.
- Bugey: This plant, on the Rhône River, is notable for its early role in France’s nuclear program.
-
Southern France: The south of France, with its Mediterranean coastline, also hosts several nuclear power plants:
- Golfech: Located near the Garonne River, this plant plays a significant role in supplying electricity to the region.
- Cruas: Situated on the Rhône River, this facility boasts four reactors and is a major contributor to France’s energy independence.
- Paluel: Located on the coast near the English Channel, this plant features four reactors and is a significant source of electricity for the Normandy region.
Historical Evolution of France’s Nuclear Program:
France’s nuclear journey began in the late 1950s, driven by a desire for energy independence and a response to the oil crisis of the 1970s. The country’s commitment to nuclear power led to the construction of numerous reactors, culminating in a peak of 58 operating reactors in the early 2000s.
The Benefits of France’s Nuclear Power Reliance:
France’s heavy reliance on nuclear power has brought about several notable advantages:
- Energy Independence: Nuclear energy has significantly reduced France’s dependence on fossil fuels, particularly oil and gas, enhancing its energy security.
- Low Carbon Emissions: Compared to fossil fuels, nuclear power plants generate electricity with significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to France’s efforts in combating climate change.
- Reliable Power Supply: Nuclear power plants are known for their consistent and reliable energy production, ensuring a stable electricity supply for the country.
- Economic Benefits: The nuclear industry provides numerous jobs and contributes significantly to France’s GDP, bolstering the national economy.
Challenges and Concerns:
Despite its benefits, France’s nuclear power program faces several challenges and concerns:
- Waste Management: The safe and secure disposal of nuclear waste remains a complex and ongoing issue, requiring careful management and long-term solutions.
- Nuclear Safety: Ensuring the safety of nuclear power plants is paramount, and incidents like the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 and the Fukushima Daiichi disaster in 2011 highlight the potential risks associated with this technology.
- Public Perception: Public opinion towards nuclear power in France has become increasingly divided, with concerns over safety, waste disposal, and the potential for accidents.
- Cost Considerations: The construction and maintenance of nuclear power plants are expensive, requiring significant financial investment and raising questions about the long-term economic viability of this energy source.
- The Future of Nuclear Power: The future of nuclear power in France is a subject of ongoing debate, with discussions revolving around the potential for new reactor technologies, the decommissioning of aging plants, and the role of nuclear energy in the transition to a low-carbon future.
FAQs: Exploring Nuclear Power in France
Q: What is the current status of nuclear power in France?
A: France currently operates 56 nuclear reactors, with several older plants scheduled for decommissioning in the coming years. The government has announced plans to reduce the share of nuclear power in the energy mix to 50% by 2035.
Q: What are the main types of nuclear reactors used in France?
A: France primarily uses Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRs), a widely adopted design known for its safety and efficiency.
Q: What are the environmental impacts of nuclear power in France?
A: Nuclear power plants generate low levels of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to the fight against climate change. However, the management of nuclear waste and the potential for accidents remain environmental concerns.
Q: What are the future prospects for nuclear power in France?
A: The future of nuclear power in France is uncertain, with debates ongoing about the potential for new technologies, the decommissioning of aging plants, and the role of nuclear energy in a low-carbon future.
Tips for Understanding France’s Nuclear Power Landscape:
- Explore maps and data: Utilize interactive maps and data visualizations to gain a visual understanding of the distribution of nuclear power plants across France.
- Consult official sources: Seek information from official sources such as the French Ministry of Energy Transition and the French Nuclear Safety Authority (ASN).
- Engage in discussions: Participate in online forums and discussions to learn from experts and engage in informed dialogue about the challenges and opportunities of nuclear power in France.
Conclusion:
France’s nuclear power landscape is a complex and evolving one. While nuclear energy has played a crucial role in providing energy independence and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, it also presents challenges related to waste management, safety, and public perception. The future of nuclear power in France will depend on the country’s ability to address these challenges and navigate the evolving energy landscape. As France continues to grapple with the complexities of nuclear energy, it is crucial to engage in open and informed dialogue about its role in the country’s energy future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into France’s Nuclear Power Landscape: A Map of Energy Independence and Environmental Impact. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!