Armenia: A Landlocked Nation in the Caucasus
Related Articles: Armenia: A Landlocked Nation in the Caucasus
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Armenia: A Landlocked Nation in the Caucasus. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Armenia: A Landlocked Nation in the Caucasus

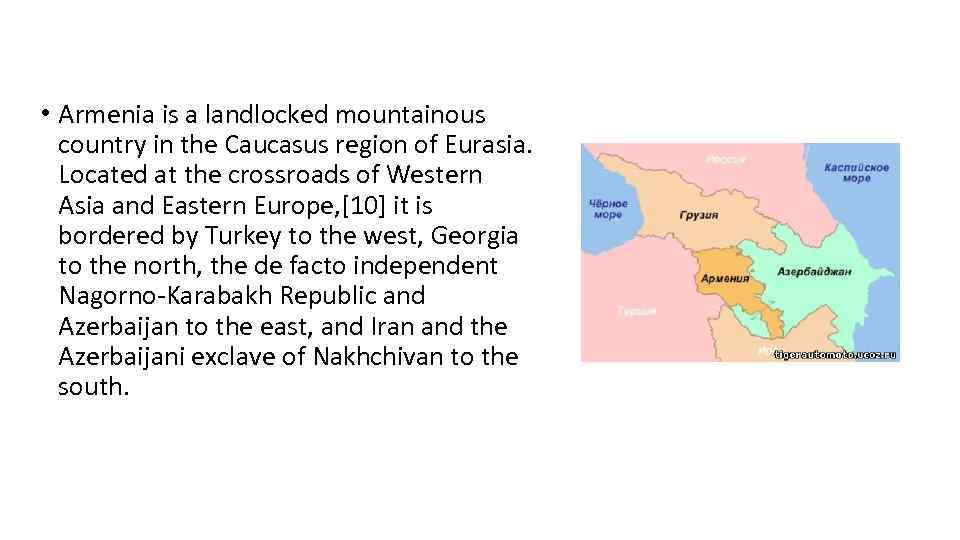
Armenia, a landlocked nation in the Caucasus region, is a country rich in history, culture, and natural beauty. Its strategic location, nestled between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, has played a significant role in shaping its history and its present-day identity.
Geographical Context:
Armenia occupies a relatively small area of 29,800 square kilometers, situated in the heart of the Caucasus Mountains. Its mountainous terrain, with an average elevation of 1,800 meters, presents a unique landscape characterized by deep valleys, volcanic plateaus, and snow-capped peaks. This geographical feature has historically influenced the development of Armenian culture and its people’s resilience.
Regional Significance:
Armenia’s location within the Caucasus region grants it a vital position as a bridge between Europe and Asia. This strategic placement has historically made Armenia a crossroads for trade routes, cultural exchange, and political influence. The country shares borders with Turkey, Georgia, Azerbaijan, and Iran, creating a dynamic and complex regional landscape.
Historical Perspective:
Armenia’s history is intertwined with its geographical location. Its ancient civilization, dating back to the 3rd millennium BC, flourished in the fertile valleys of the Ararat Plain, a region of immense historical and cultural significance. The Armenian Highlands, encompassing the modern-day territory of Armenia, served as a cradle for the development of Armenian culture, language, and identity.
Modern-Day Armenia:
Today, Armenia is a sovereign nation with a vibrant culture and a rich history. Its strategic location continues to play a significant role in its economic and political development. The country strives to strengthen its ties with its neighboring countries while also pursuing its own path towards economic growth and regional integration.
Key Geographic Features:
- Mount Ararat: This iconic mountain, although currently located in Turkey, holds immense symbolic significance for Armenians as it is believed to be the resting place of Noah’s Ark.
- Lake Sevan: This largest freshwater lake in the Caucasus region is a vital source of water for Armenia and a popular tourist destination.
- The Ararat Plain: This fertile plain, located in the southwest of Armenia, is a major agricultural region and a site of historical significance.
- The Armenian Highlands: This mountainous region, encompassing Armenia and parts of neighboring countries, played a crucial role in the development of Armenian culture and identity.
Cultural Significance:
Armenia’s location has contributed to its unique cultural identity. It has been influenced by neighboring civilizations, including Persia, Byzantium, and the Ottoman Empire, while also retaining its distinct cultural heritage. Armenian art, music, literature, and cuisine reflect this rich cultural tapestry.
Economic Significance:
Armenia’s strategic location offers potential for economic development. The country is striving to establish itself as a regional hub for trade and investment. Its natural resources, including copper, gold, and molybdenum, are vital to its economic growth.
Political Significance:
Armenia’s location in a politically complex region presents both challenges and opportunities. The country seeks to maintain its independence while also fostering regional cooperation and stability. Its historical ties with Russia, its membership in the Eurasian Economic Union, and its ongoing negotiations with Azerbaijan regarding the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict all highlight the complexities of its geopolitical landscape.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While Armenia’s location offers potential for development, it also presents significant challenges. The country faces issues related to economic development, political stability, and regional security. The unresolved conflict with Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh remains a major obstacle to peace and stability in the region.
FAQs about Armenia’s Location:
1. Is Armenia a landlocked country?
Yes, Armenia is a landlocked country. It is located in the Caucasus region, surrounded by Turkey, Georgia, Azerbaijan, and Iran.
2. What are the major geographical features of Armenia?
Armenia is characterized by its mountainous terrain, with the Caucasus Mountains dominating its landscape. Key geographical features include Mount Ararat, Lake Sevan, the Ararat Plain, and the Armenian Highlands.
3. What is the historical significance of Armenia’s location?
Armenia’s location has played a crucial role in its history, making it a crossroads for trade routes and cultural exchange. Its ancient civilization flourished in the fertile valleys of the Ararat Plain, and the Armenian Highlands served as a cradle for the development of Armenian culture and identity.
4. What are the economic implications of Armenia’s location?
Armenia’s location offers potential for economic development, as it can serve as a regional hub for trade and investment. Its natural resources, including copper, gold, and molybdenum, are vital to its economic growth.
5. What are the political challenges and opportunities associated with Armenia’s location?
Armenia’s location in a politically complex region presents both challenges and opportunities. The country faces issues related to economic development, political stability, and regional security. The unresolved conflict with Azerbaijan over Nagorno-Karabakh remains a major obstacle to peace and stability in the region.
Tips for Understanding Armenia’s Location:
- Study a map: A clear understanding of Armenia’s location on a world map is crucial for comprehending its geographical context.
- Research its neighboring countries: Understanding the political and cultural dynamics of Armenia’s neighboring countries provides valuable insights into its regional significance.
- Explore its history: Delving into Armenia’s rich history, particularly its ancient civilization and its strategic role in the region, sheds light on the factors that shaped its present-day identity.
- Learn about its culture: Exploring Armenian culture, including its art, music, literature, and cuisine, reveals the diverse influences that have shaped its unique identity.
- Stay informed about current events: Keeping abreast of current events in the Caucasus region, including the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, provides a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities facing Armenia.
Conclusion:
Armenia’s location in the Caucasus region is a defining feature of its history, culture, and present-day identity. Its strategic position as a bridge between Europe and Asia has shaped its cultural heritage, influenced its economic development, and presented both challenges and opportunities in its political landscape. Understanding Armenia’s location is key to appreciating its unique place in the world and its ongoing journey towards peace, stability, and economic prosperity.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Armenia: A Landlocked Nation in the Caucasus. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!